What is Apical Resection?
Apical resection is the removal of the cyst or infection that occurs in the root of the tooth by cutting off the tooth root by operation. How long are teeth used with apical resection?, will another treatment be required after the operation?, the questions are the questions that preoccupy the patients' heads.
Under what circumstances is Apical Resection Applied?
A cyst or infection in the root of the tooth usually occurs in cases where canal treatment fails. The most common causes of failure are; overflow of the duct fill from the root end, incomplete filling of the root canals, and the root canal contains non-found side branches. Antibiotic therapy is not sufficient at this stage because the cause of the infection has not disappeared. The infection should be surgically intervened and cleaned into the tooth.
Should Teeth Be Withdrawn Instead of Apical Resection Treatment?
Apical resection is applied for the purpose of saving the female instead of pulling it. Shooting or apical resection? The important criterion for making a decision is the length of the tooth root. If the tooth root is shorter than normal, pulling the tooth may be a more successful treatment, as 1/3 of the root will also be taken with infection or cyst. In apical resection, 2/3 part of the teeth should remain intact.
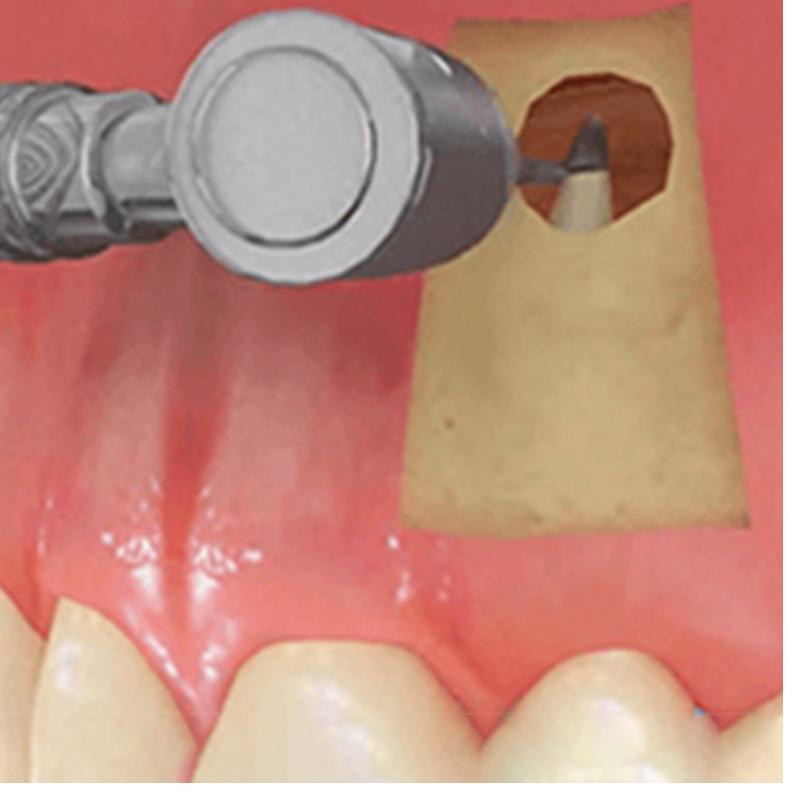
How to Apply Apical Resection?
Under local anesthesia, the root tip is completely exposed by the incision opened from the gums. Patient and inflamed tissues, such as cysts or infections, are cut together with the root tip part and the root canal is cleaned and refilled. Gums are sewn and the operation is completed. Depending on the healing process of the patient, the gums return to normal after the last period. The space created in the bone will be replaced by the new bone after a few months.
How Much Are Teeth Treated for Apical Resection Used?
After apical resection, the condition of the intact tooth is checked by the dentist. In the 3rd month, 6th month, 12th month and 24th months, x-rays are taken care of and new bone formation is observed around the root. Treatment of teeth that do not cause any problems within two years is considered successful.
